Gameplay Screenshots
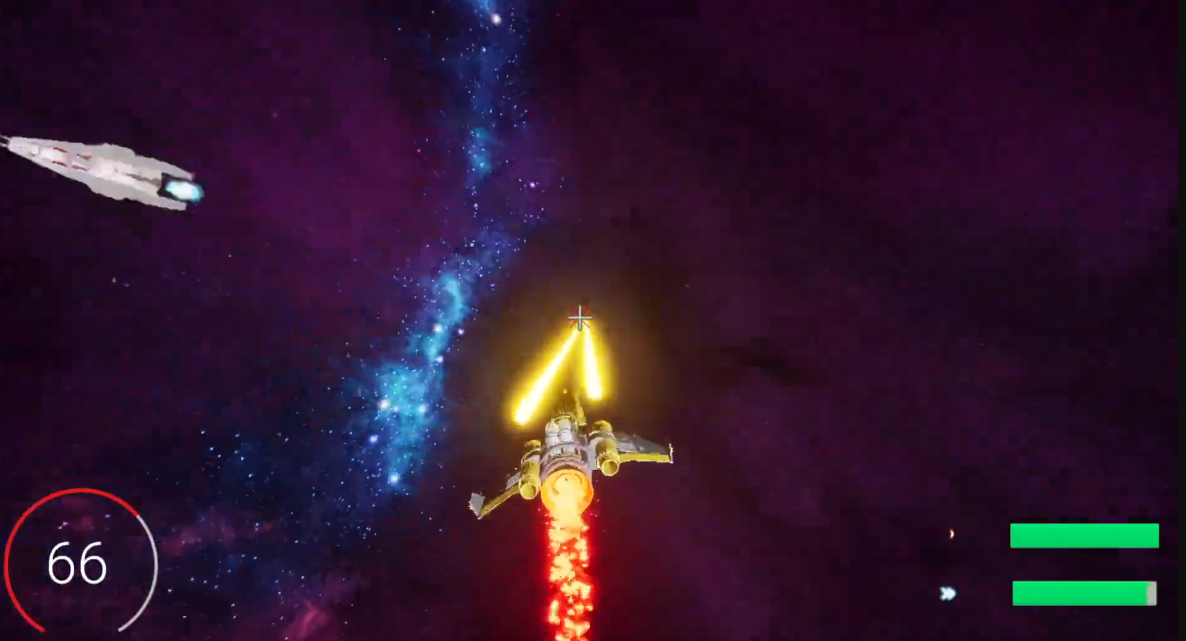




Showcase
Highlighting
1. PathFinding
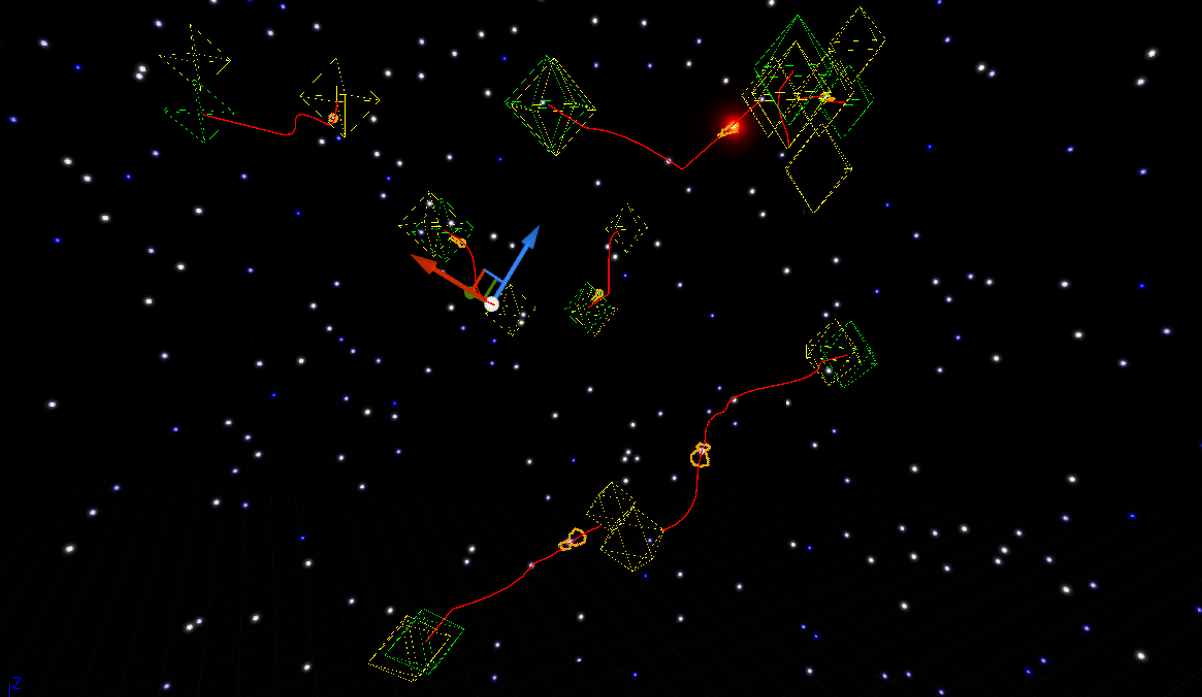
The pathfinding algorithm that was applied in this project was the A* algorithm. Here is a very good educational video that helped me have a better understanding of how the A* algorithm works and also served as a reference for this project.
PathGrid
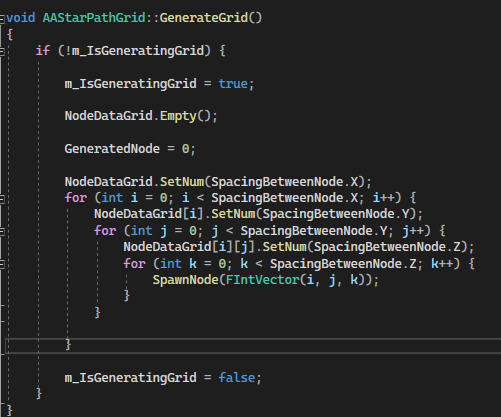
Pathfinding grid is the core pathfinding component that acts like a NavMeshBoundsVolume. A set of node data will be generated and stored as a 3-dimensional index.
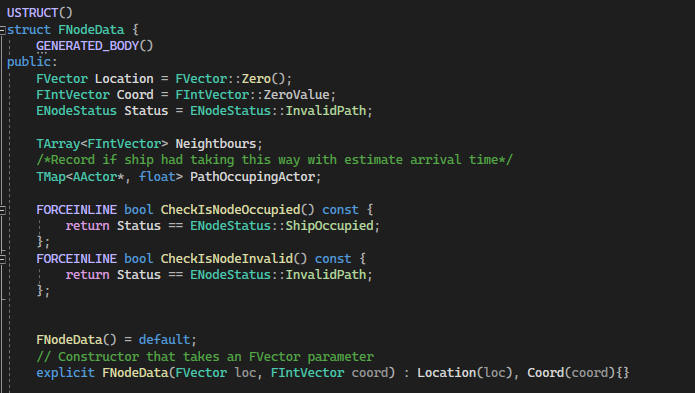
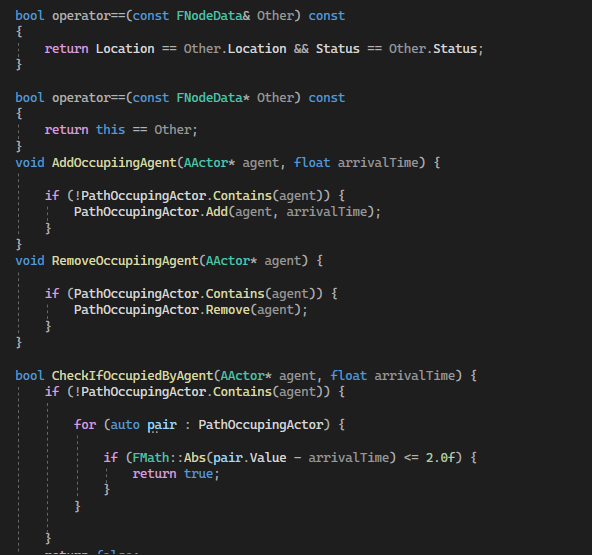
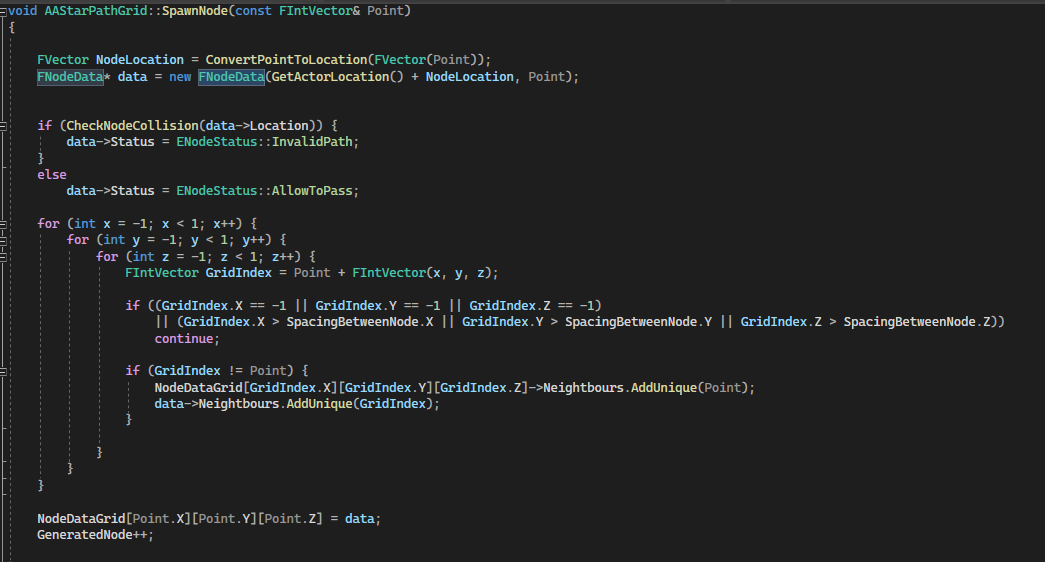
Node data is a struct that stores the world location, its own coordinate (the index representation in 3-dimensional array), the node status, the neighbor nodes index and tracking moving player. When a node was spawning, a collision check would happen in order to know if anything was blocking the node location, avoid the unavailable node bring into consideration of path finding algorithm.
AStarAgentComponent
After the foundation of the path finding was build, it is time to make AI move which is where I implemented the A* Algorithm. Before I start showcase about the core logic of algorihtm, let me introduce another struct that will be used in this algorithm
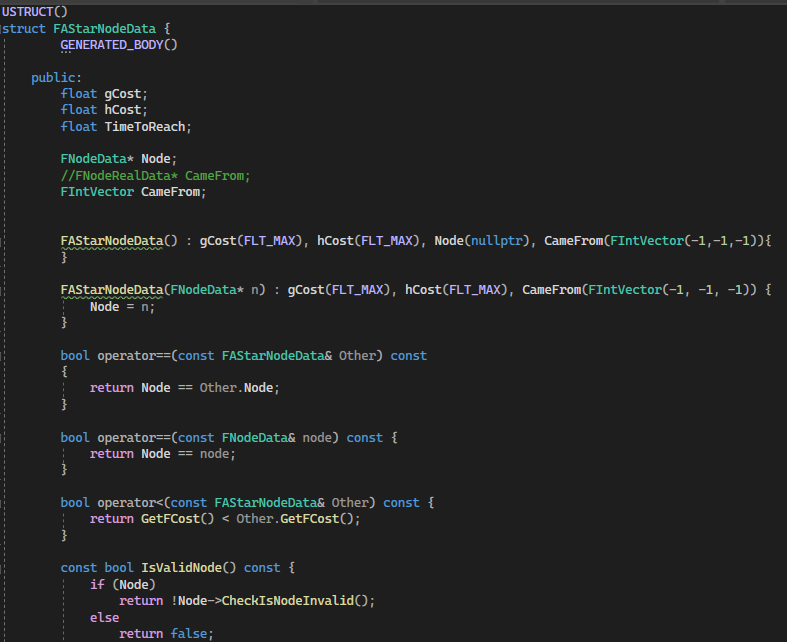
FAstarNodeData is a struct that is used to construct the path from the start location to the end location. It stores the GCost (represent the cost from last node to this node), FCost (represent the cost from start node to this node), camefrom node index, the current node pointer and also time to reach.
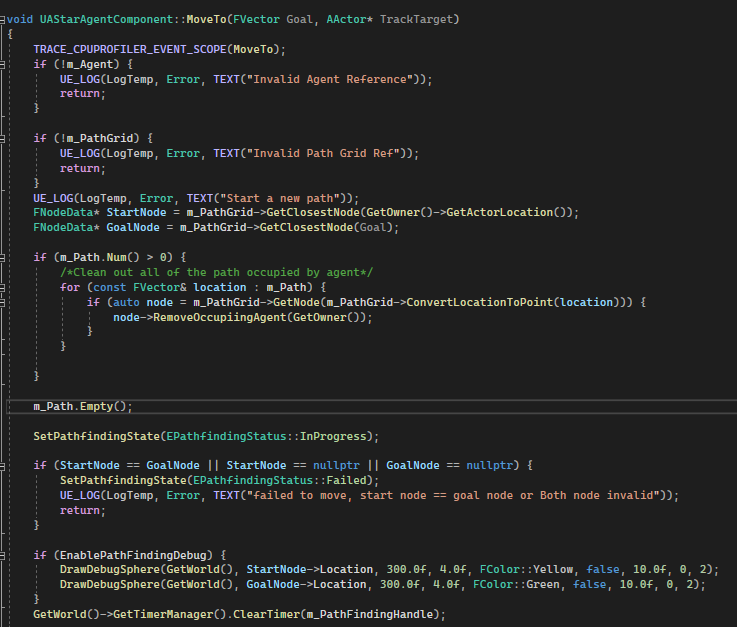
MoveTo is the core logic function that make the AI move. Before A* algorithm start, system will define the start node and end node based on current AI location. GetClosestNode() convert the world location into node coordinate to so the program will know the node explicitly without looping through the node dimension array.
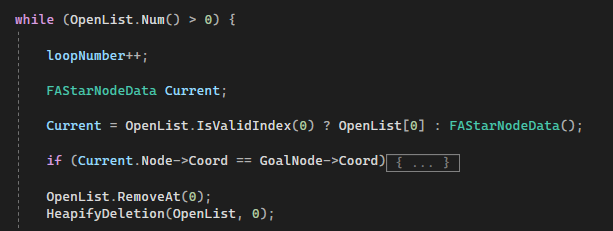
Once start node and end node was defined, A* algorithm will start. OpenList will be the list that used to store all the potential node to travel while ClosedList will be final list that gonna used to construct the path. A local variable CurrentNodeData will be used to define the current start node location and store inside the ClosedList .
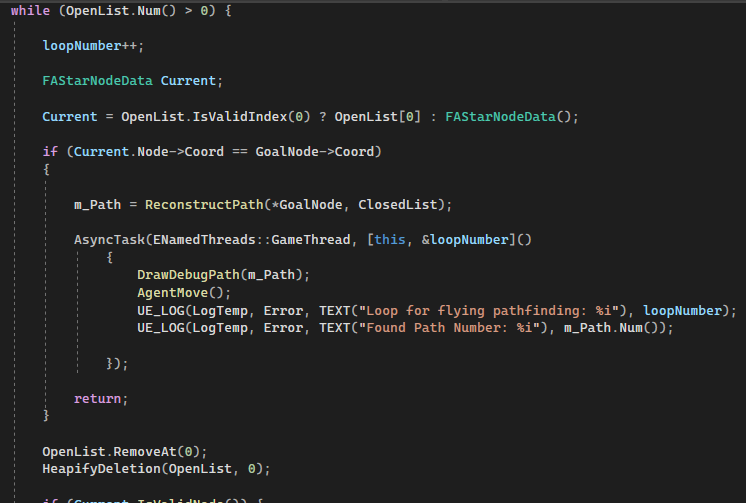
Next, start a while loop, keep looping until either there is no potential node or the program finds the Goal Node. The first OpenList element will be decided as the current node. Note that the first element of OpenList will always be the lowest cost node to travel.
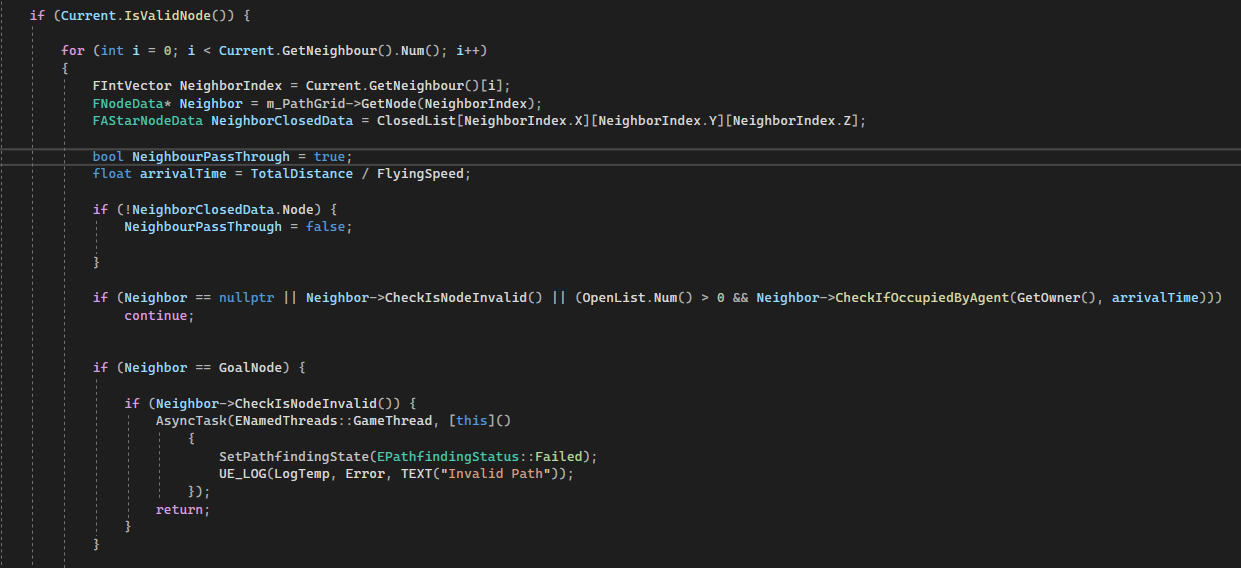
If the current node is valid, start finding the next node with the neighbor node. If the neighbor node is valid and passes every false check, the program will continue to the next process of calculating navigation cost.
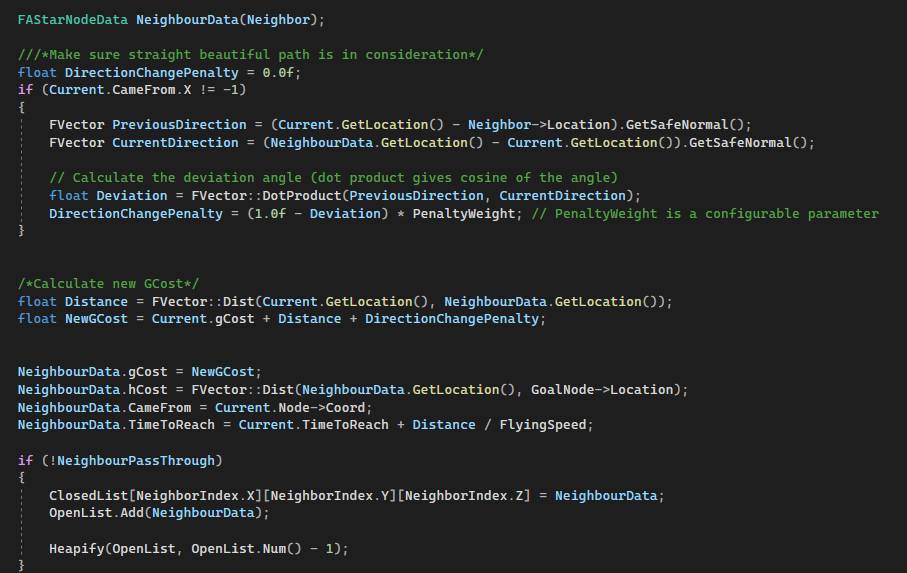
Here, the program starts calculating the navigation cost. The navigation cost will be affected by DirectionChangePenalty and Distance. Both of the values will decide the GCost value and eventually affect the navigation since navigation construction will always require choosing the shortest and lowest cost path.
It is worth mentioning the effect of DirectionChangePenalty is to prevent and eliminate the chance of navigation that is against the current path direction. It will try to provide a smooth and natural path.
After Neighbour Data finish setup, if neighbour not been passed through by the previous iteration, this node should be stored into OpenList and ClosedList. Then Heaptify function will put the lower cost node as first element in the OpenList.
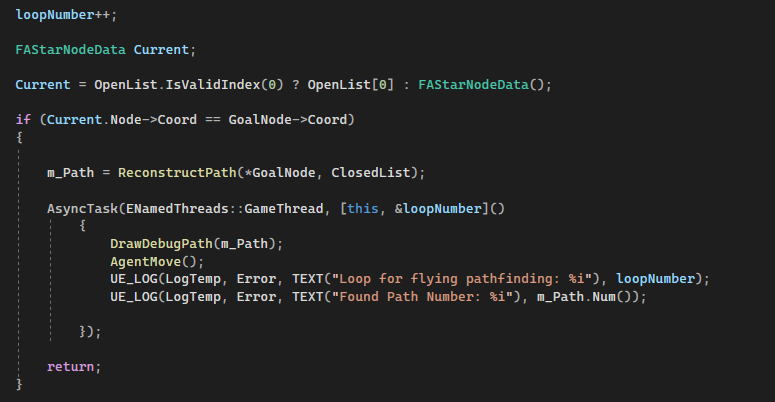
Finally, the program starts a new iteration. If the current node is goal node, path will reconstruct and pass into the GameThread for AI to move.
Reconstruct
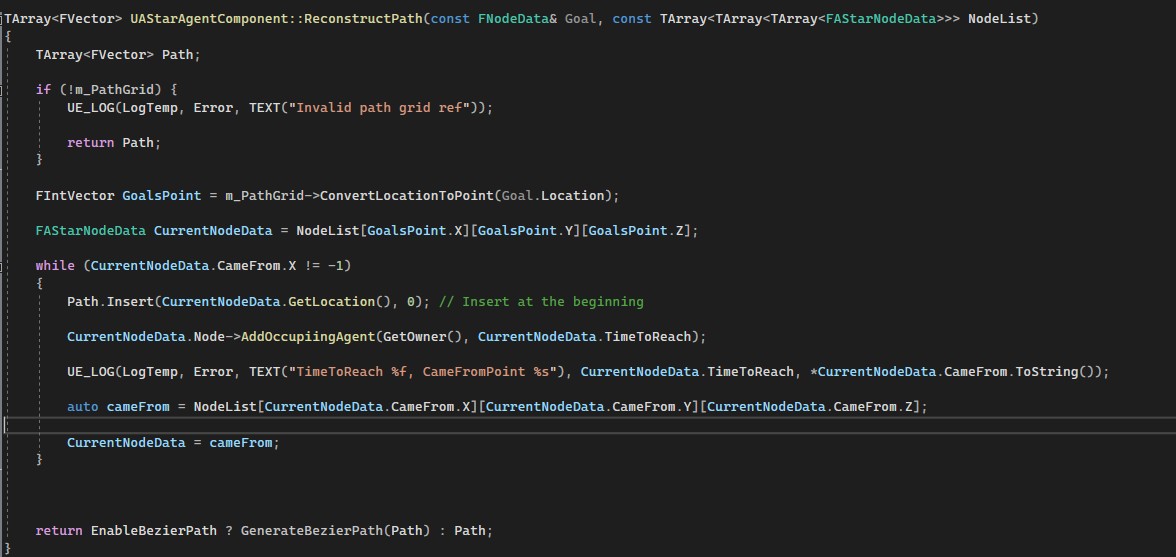
In the ReconstructPath function, the path will construct by starting with the goal node and tracking back the came from node until it meets the begin node. Over the ReconstructPath function, it will notice the path grid that each node will be occupied by the agent and also their arrival time.
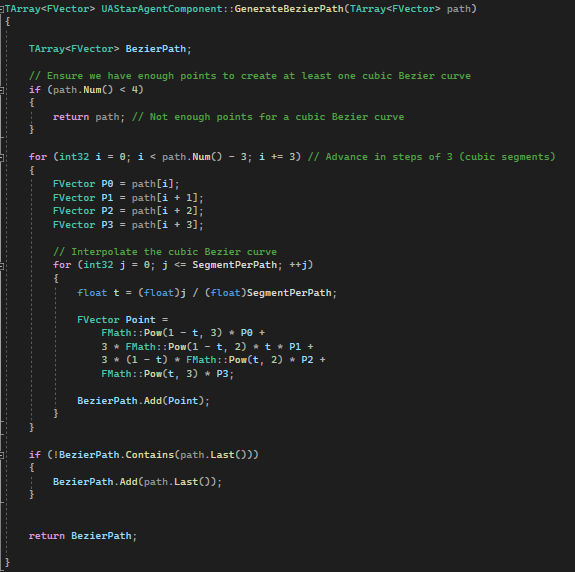
In order to have a smooth path, bezier curve will be applied to agent vector output.
Optimization
Optimization is very crucial and one of the very first problems I encounter after finishing the pathfinding algorithm. The navigation iteration will increase along with the detail of pathfinding and the number of node in the path grid. The heavy iteration can even block the game thread during early development. Therefore, in order to increase the iteration speed and make sure the heavy iteration won't block the game thread, heapify and multithreading were applied to the navigation system.
1. MultiThreading
This is the very first time that I actually applied multithreading in Unreal Engine. My past experience was mostly related to gameplay, AI and feature development, multithreading wasn't a necessary tool. However, to implement such a heavy looping algorithm, moving this process to the background thread seems to be a logical approach to increase speed and efficiency.
2. Heapify
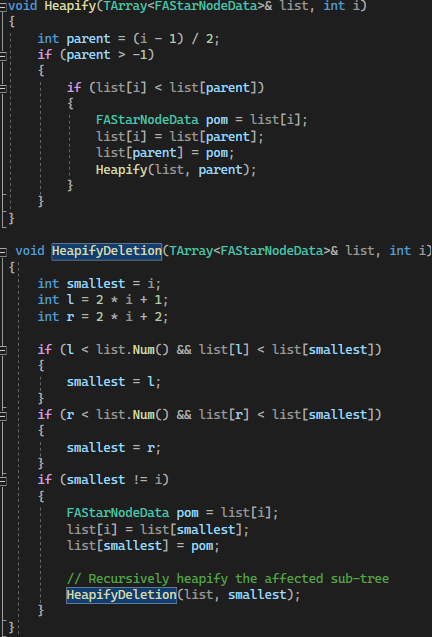
Other than multithreading, the second tool that I used was Heapify. The purpose of this function was to find the lowest cost node and put it on top of the list. Initially, FindByPredicate function was used to find the lowest cost but it was too slow. So in the end, it was being replaced by the Heapify function which is much faster than the FindByPredicate.
2. Spaceship Character
Spaceship Character, the base class of both player and enemy class. It contain the general function of character such as:
Weapon Shooting
Health and Damage Taken Feature
Mesh setup
Player
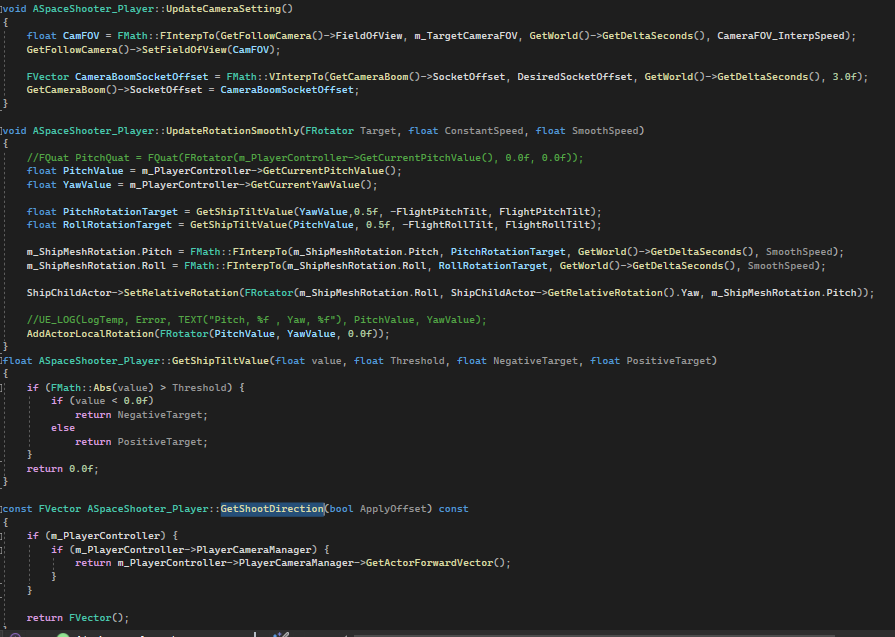
The notable part of player class is the smooth rotation of character and smooth FOV of the camera. The FOV of the camera will fit with the speed of the character. The rotation of player spaceship will ignore gimbal lock, so players are allowed to rotate pitch and roll 360 degrees.
Enemy
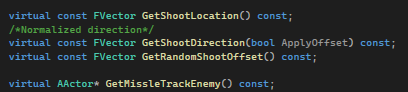
The only part different for enemy will be the different output of shoot direction. Enemy also possess the AStarAgentComponent so enemy was allowed to move freely in 3D space pathfinding.
Data Management
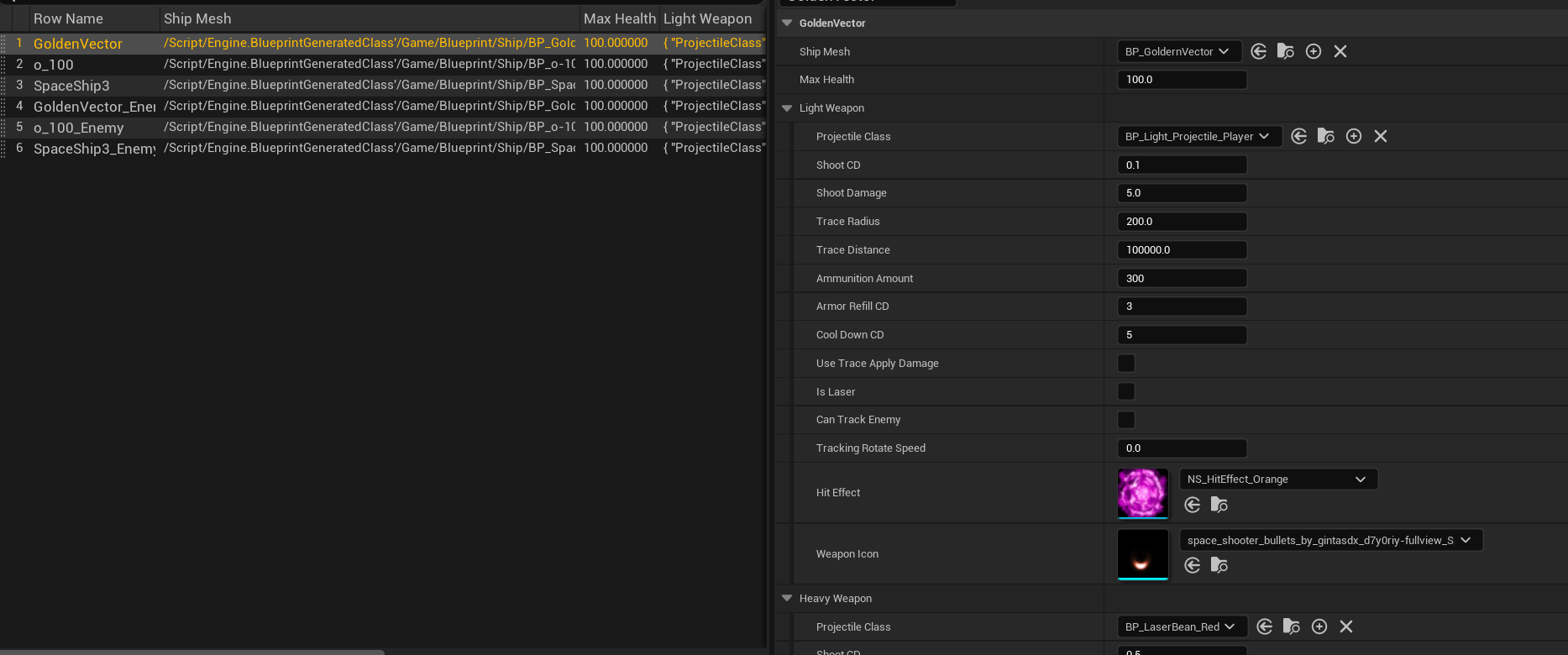
The character stat, weapon variable and mesh will be managed in Data Table.
